Lymphoma is a type of cancer that begins in infection-fighting cells of the immune system. These cells are known as lymphocytes and found in the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and other parts of the body.
There are two main types of lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the most prevalent with the majority of people with lymphoma having this type. The other variant is Hodgkin lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma involve different types of lymphocyte cells. Every type of lymphoma grows at a different rate and responds differently to treatment.
Prevalence
The age-adjusted incidence rates for Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in men and women in India are 2.9 per 100,000 population and 1.5 per 100,000, respectively. These are about one quarter of the incidence rates reported from Western Europe or North America. Though incidence rates are lower in India, the average age of onset is 54, almost a decade earlier than that of western nations.
The disease is most prevalent among the elderly, or within the age group of fifteen to forty. It is also notably higher in the male population.
The exact cause of the condition is unknown, though several risk factors are well-documented. Urban populations are at a higher risk, suggesting a potential link to air pollution. Incidence rates are far higher within cities in India.
Rural populations are not free of risk factors. Exposure to benzene or chemicals that kill insects and weeds has also been linked to the development of lymphoma. These chemicals may be commonly encountered in rural farm workers as typical components of insecticides.
Symptoms
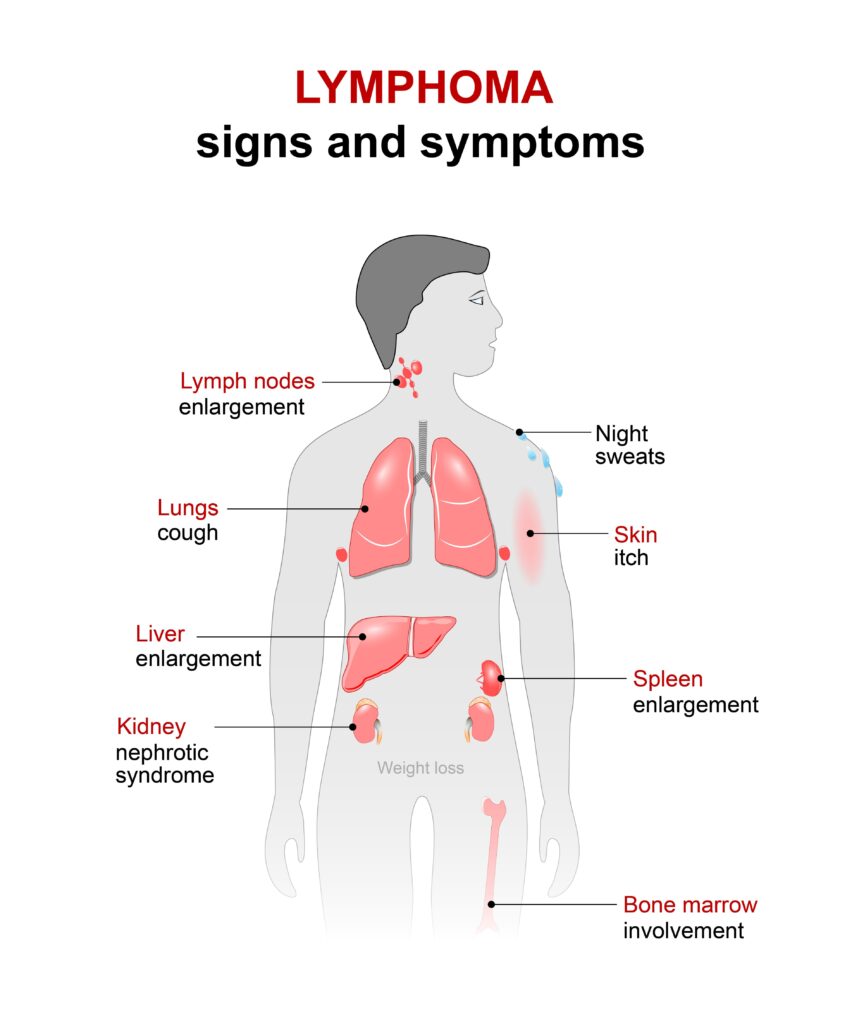
One of the most prominent signs of lymphoma is swollen glands (lymph nodes), often in the neck, armpit, or groin that are painless. This is a complication that can occur in numerous diseases and infections. As such it is necessary to seek out the opinion of a trained doctor if these symptoms occur.
Other easily mistaken symptoms are predominant traits of lymphoma. Coughing, shortness of breath and fever can all occur, and may be easily mistaken for the flu or a cold.
Lymphoma can be lethal in its later stages, as the cancer can spread to other organs and cause far more serious issues. As such it is vital that it is caught in its early stages as treatment prospects are far better.
Treatment
As with many other forms of cancer the standard treatments for lymphoma include chemotherapy, immunotherapy or radiation therapy. This will hopefully destroy the rapidly replicating cancer cells. However, as this can also destroy healthy stem cells within the body, a stem cell transplant may also take place after a bout of aggressive chemotherapy.
As there is no centralised tumour, surgery is not utilised in its treatment.