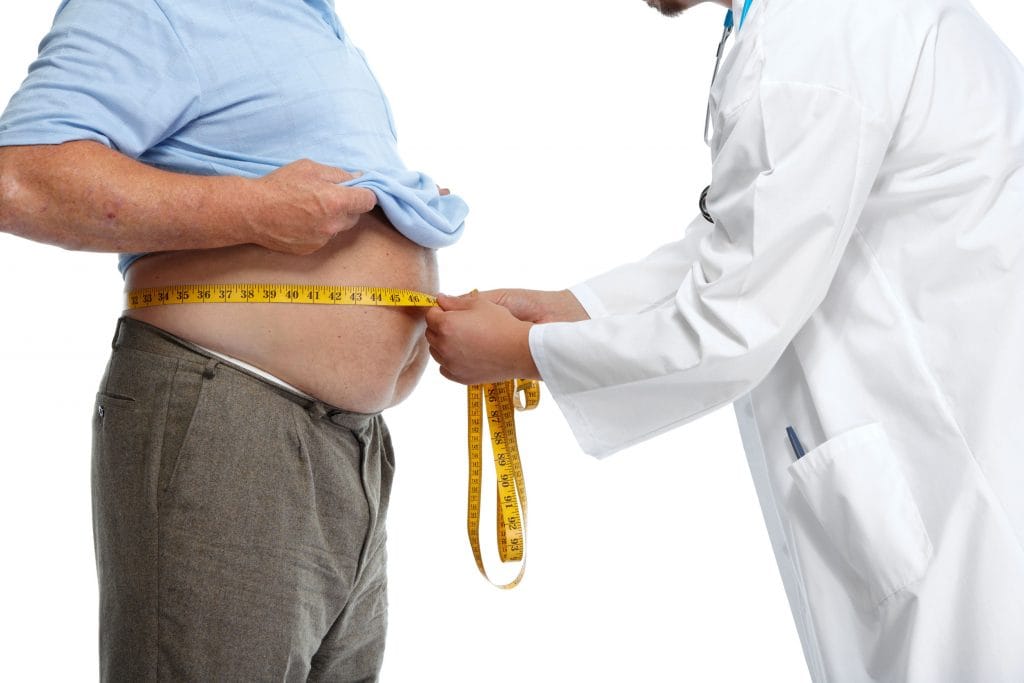
Obese COVID-19 patients are at heightened risk of complications, medicos in Telangana state capital Hyderabad have warned.
Doctors in the city observed that obese patients accounted for at least thirty percent of those affected by COVID-19 – the disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or, simply, coronavirus. For India, a country facing a growing crisis of obesity, this is far from good news.
More than 135 million Indians are obese, with the condition no longer limited to one of the affluent. As previously reported by Health Issues India, “research indicates that economic growth correlates with fewer cases of stunting and wasting, both conditions linked to undernourishment, but also with higher obesity rates. Greater availability of processed produce and fast food contributing to increased consumption of so-called ‘westernised’ diets, a transition in employment from manual labour to white collar work, and lesser levels of physical activity are other factors.
“The effects, meanwhile, are widespread and far-reaching. Obesity negatively affects productivity and educational performance, impairing economic growth. For the individual, meanwhile, obesity has numerous deleterious health effects, upping the risk of numerous noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease – India’s most common cause of death and one which is already increasing in prevalence. Already, children in India are witnessing higher risk of conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol. More than ten percent of children in India are prediabetic.”
The link identified by Hyderabad’s doctors between COVID-19 and obesity adds fuel to the fire. Not only is the disease a risk factor for NCDs, it now seems to be a risk factor for serious complications of a potentially lethal virus.
One in five people globally are at risk of serious complications of COVID-19, research suggests. As we learn more about the disease, understanding the comorbidities and conditions that could amplify the risk of severity and mortality will be vital in how we respond to the pandemic. c